publications
2026
-
 The geography of climate concern: A large-scale analysis of public discourse on extreme heat in China using social media and explainable AIPu Zhang, Yiliang Li, Zheng Wei, and 1 more authorEnvironmental Impact Assessment Review, 2026
The geography of climate concern: A large-scale analysis of public discourse on extreme heat in China using social media and explainable AIPu Zhang, Yiliang Li, Zheng Wei, and 1 more authorEnvironmental Impact Assessment Review, 2026As extreme heatwaves intensify into a primary public health threat under climate change, understanding the dynamics of public perception is critical for effective risk communication. While traditional methods are limited in scale and timeliness, social media offers an unprecedented real-time window into public discourse. This study provides the first large-scale, computational analysis of Chinese public discourse on extreme heat, leveraging 348,417 user comments from the platform Douyin. After addressing multicollinearity through a rigorous variable reduction process, our novel framework combines a Large Language Model (LLM) for thematic classification with an FDR-corrected regression model and an explainable AI (SHAP) analysis to identify and interpret the drivers of public concern. Thematically, we find a stark divergence between the most frequent topics (e.g., regional comparisons) and the most publicly endorsed topics (e.g., fatalism and mutual care), revealing latent community values. Our regression analysis, corrected for multiple comparisons, reveals a powerful and statistically robust link: higher maximum temperatures directly drive increased public discourse on both “Health Impacts” and “Entertainment and Emotional Venting.” The SHAP analysis provides a deeper layer of insight, revealing that underlying geographical context (i.e., average elevation) and socioeconomic status exert the greatest overall influence on the nature of the conversation, shaping everything from tourism-related discussions to expressions of social vulnerability. These findings demonstrate that public discourse on heat is shaped by a hierarchy of factors, from statistically robust climate triggers to highly impactful socioeconomic and geographical contexts. This work provides a scalable framework for a dynamic Social and Health Impact Assessment (SIA/HIA), underscoring the need for tailored communication strategies that account for both environmental exposure and social vulnerability.
@article{PZHANG05, title = {The geography of climate concern: A large-scale analysis of public discourse on extreme heat in China using social media and explainable AI}, journal = {Environmental Impact Assessment Review}, volume = {117}, pages = {108227}, year = {2026}, issn = {0195-9255}, publisher = {Elsevier BV}, doi = {10.1016/j.eiar.2025.108227}, dimensions = {true}, url = {https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S019592552500424X}, author = {Zhang, Pu and Li, Yiliang and Wei, Zheng and Hui, Pan}, keywords = {Extreme heat, Social media, Environmental impact assessment, Explainable AI, Geospatial analysis, Climate communication, Environmental justice} } -
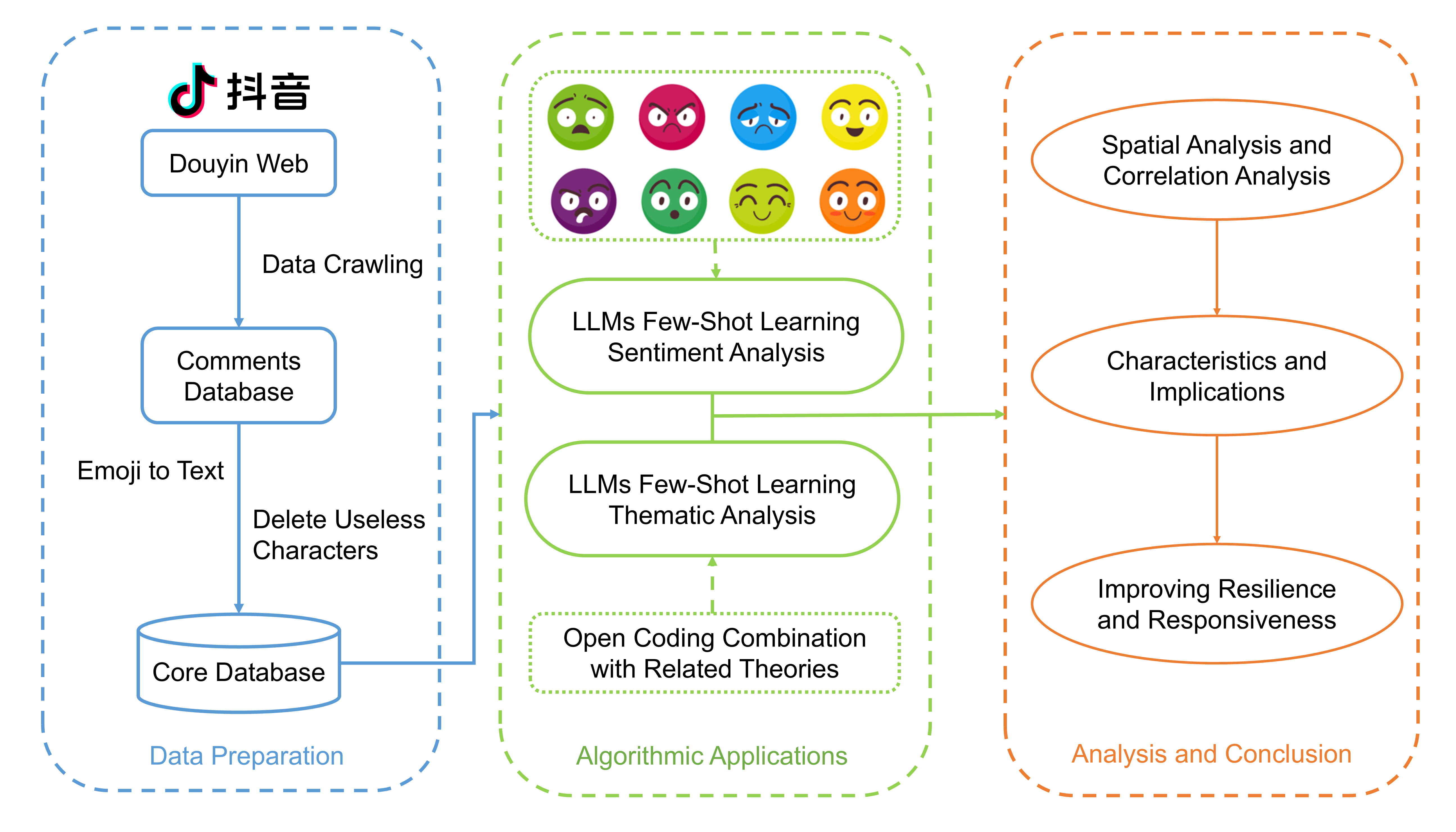 Reconfiguring Responsibility: An Empirical Analysis of Crisis Discourse and Situational Crisis Communication on DouyinPu Zhang, Zheng Wei, and Feng KongInternational Journal of Disaster Risk Science, Jan 2026
Reconfiguring Responsibility: An Empirical Analysis of Crisis Discourse and Situational Crisis Communication on DouyinPu Zhang, Zheng Wei, and Feng KongInternational Journal of Disaster Risk Science, Jan 2026The public’s attribution of responsibility during a crisis is a central process in crisis communication,often explained by the situational crisis communication theory (SCCT). However,SCCT was developed in a pre-social media era,and its applicability in the new ecosystem of algorithm-driven,short-video platforms remains a critical theoretical gap. This study investigated how the core mechanisms of public responsibility attribution are reconfigured in the unique context of China’s leading short-video platform,Douyin. Analyzing 185,148 comments following the tragic Yingcai School fire,our large language model (LLM)-based analysis answered two questions: (1) How are public attributions of responsibility structured in this emotionally charged,algorithmic environment? and (2) How do offline socioeconomic factors shape these digital crisis discourses? Our findings reveal two distinct attribution pathways,namely an anger-accountability track and a sadness-reflection track and demonstrate that critical discourse is systematically linked to regional development. This research provides a crucial empirical validation of SCCT for the short-video era and offers a data-driven guide for context-aware public administration.
@article{PZHANG06, title = {Reconfiguring Responsibility: An Empirical Analysis of Crisis Discourse and Situational Crisis Communication on Douyin}, issn = {2192-6395}, url = {http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s13753-026-00693-2}, doi = {10.1007/s13753-026-00693-2}, journal = {International Journal of Disaster Risk Science}, publisher = {Springer Science and Business Media LLC}, author = {Zhang, Pu and Wei, Zheng and Kong, Feng}, year = {2026}, month = jan, } - Beyond Aggregate Feedback: A Spatially-Aware Computational Framework for Understanding Citizen-State Interaction on Social MediaPu Zhang, Zheng Wei, Muzhi Zhou, and 2 more authorsACM Transactions on Social Computing, Jan 2026
In the era of digital governance, social media platforms have become critical arenas for citizen-state interaction and policy feedback. However, governments often struggle to translate massive, unstructured public discourse into actionable intelligence, frequently relying on aggregated metrics that obscure critical regional nuances. This study introduces a spatially-aware computational framework to bridge this gap. Integrating Large Language Model (LLM) based few-shot learning with SHAP (SHapley Additive exPlanations) and GIS analysis, we examine the public reception of China’s 2025 national childcare subsidy policy using a dataset of 352,448 comments. Our analysis reveals a stark divergence between information-seeking behaviors (high volume) and substantive legitimacy debates (high engagement). Crucially, we demonstrate that the socioeconomic drivers of this discourse—such as gender ratios and educational attainment—are highly spatially heterogeneous, necessitating distinct governance responses across different regions. This research contributes to the field of government information systems by validating a novel, replicable methodology for precision policy analytics, offering policymakers a tool to move beyond national averages and achieve more responsive, context-specific governance.
@article{TSC2026, author = {Zhang, Pu and Wei, Zheng and Zhou, Muzhi and Evans, James and Hui, Pan}, title = {Beyond Aggregate Feedback: A Spatially-Aware Computational Framework for Understanding Citizen-State Interaction on Social Media}, year = {2026}, publisher = {Association for Computing Machinery}, address = {New York, NY, USA}, url = {https://doi.org/10.1145/3790251}, doi = {10.1145/3790251}, journal = {ACM Transactions on Social Computing}, month = jan, keywords = {E-participation, Policy Feedback, Computational Social Science, Precision Governance, SHAP, China} } - Leveraging large language models to explain provincial heterogeneity in online discussion of water pollution in China: A socioeconomic and environmental perspectivePu Zhang, Na Jiang, Yiliang Li, and 2 more authorsJournal of Cleaner Production, Jan 2026SCI Q1, IF: 10.0
China’s industrialization threatens water systems and public health. This study uses a large language model to classify 170,000 Douyin comments into nine topics and seven emotions, identifying their provincial heterogeneity. We then applied a robust Beta Regression framework—using twelve provincial predictors and controlling for spatial autocorrelation and FDR to model the drivers of this heterogeneity. The analysis reveals a striking divergence: provincial-level factors are strong predictors of what citizens discuss, but not how they feel. We identified 10 robust drivers for topics; most notably, higher provincial ’Average Schooling Years’ strongly predicts "Public Health" discourse (beta = 1.638, q < 0.001). In stark contrast, after the same rigorous correction, zero provincial variables significantly predict emotional expression (all q > 0.1). This "topic-emotion split" provides a novel solution for environmental governance, enabling agencies to tailor strategies to specific, context-driven topics rather than just generalized public emotion.
@article{PZHANG07, title = {Leveraging large language models to explain provincial heterogeneity in online discussion of water pollution in China: A socioeconomic and environmental perspective}, journal = {Journal of Cleaner Production}, volume = {543}, pages = {147517}, year = {2026}, issn = {0959-6526}, doi = {10.1016/j.jclepro.2026.147517}, url = {https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0959652626000569}, author = {Zhang, Pu and Jiang, Na and Li, Yiliang and Wei, Zheng and Hui, Pan}, publisher = {Elsevier BV}, note = {SCI Q1, IF: 10.0}, keywords = {Digital platforms, Social media Analytics, Public sentiment analysis, Environmental governance, Social computing} }
2025
- ContextAware: a multi-agent framework for detecting harmful image-based comments on social mediaZheng Wei, Mingchen Li, Pu Zhang, and 3 more authorsIn Proceedings of the Thirty-Fourth International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence , Montreal, Canada, Jan 2025IJCAI 2025
Detecting hidden stigmatization in social media poses significant challenges due to semantic misalignments between textual and visual modalities, as well as the subtlety of implicit stigmatization. Traditional approaches often fail to capture these complexities in real-world, multimodal content. To address this gap, we introduce ContextAware, an agent-based framework that leverages specialized modules to collaboratively process and analyze images, textual context, and social interactions. Our approach begins by clustering image embeddings to identify recurring content, activating high-likes agents for deeper analysis of images receiving substantial user engagement, while comprehensive agents handle lower-engagement images. By integrating case-based learning, textual sentiment, and vision-language models (VLMs), ContextAware refines its detection of harmful content. We evaluate ContextAware on a self-collected Douyin dataset focused on interracial relationships, comprising 871 short videos and 885,502 comments–of which a notable portion are image-based. Experimental results show that ContextAware not only outperforms state-of-the-art methods in accuracy and F1 score but also effectively detects implicit stigmatization within the highly contextual environment of social media. Our findings underscore the importance of agent-based architectures and multimodal alignment in capturing nuanced, culturally specific forms of harmful content.
@inproceedings{10.24963/ijcai.2025/1103, author = {Wei, Zheng and Li, Mingchen and Zhang, Pu and Liu, Xinyu and Qu, Huamin and Hui, Pan}, title = {ContextAware: a multi-agent framework for detecting harmful image-based comments on social media}, year = {2025}, isbn = {978-1-956792-06-5}, url = {https://doi.org/10.24963/ijcai.2025/1103}, doi = {10.24963/ijcai.2025/1103}, booktitle = {Proceedings of the Thirty-Fourth International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence}, articleno = {1103}, numpages = {9}, location = {Montreal, Canada}, series = {IJCAI '25}, note = {IJCAI 2025} }
2024
-
 How Effective is the Shorts Transformation of Traditional Media? An Analysis from the Perspective of User-Generated ContentPu Zhang, and Corey Kewei XuIn Computer Supported Cooperative Work and Social Computing , Jan 2024
How Effective is the Shorts Transformation of Traditional Media? An Analysis from the Perspective of User-Generated ContentPu Zhang, and Corey Kewei XuIn Computer Supported Cooperative Work and Social Computing , Jan 2024The digital transformation of traditional media outlets has become a critical imperative in the evolving media landscape. As traditional media grapple with the challenges of adapting to the rise of digital and social media platforms, understanding the factors that shape their performance and user engagement on these emerging channels is of paramount importance. This study examines the comparative performance of a traditional media account with a government background (Hubei Daily) and a specialized new media account (Cover News) on Douyin platform, with a focus on the distribution of emotional sentiment and thematic diversity in user-generated content. We collected 19,343 comments from “Hubei Daily,” with 18,792 valid (97.15%), and 36,737 comments from “Cover News,” with 28,910 valid (78.69%). Our research used a BERT fine-tuned model for sentiment analysis, TF-IDF for keyword extraction, keyword co-occurrence analysis, and a large language model for topic modeling. This approach allowed us to capture a wide range of discussion topics and understand the thematic focus. Findings show that the new media account covered broader topics, whereas the traditional media account had a more concentrated thematic focus. Typically, such events should generate negative emotions and discussions around accountability. However, the study indicates that users are more cautious in their comments on official media, suggesting ineffective digital transformation by traditional media. This underscores the need for traditional media to better understand and adapt to content preferences and engagement patterns of shorts platform users, highlighting the complexities of transitioning to emerging platforms and the importance of effective content strategies and meaningful user engagement.
@inproceedings{PZHANG04, author = {Zhang, Pu and Xu, Corey Kewei}, editor = {Sun, Hailong and Fan, Hongfei and Gao, Yongqiang and Wang, Xiaokang and Liu, Dongning and Du, Bowen and Lu, Tun}, title = {How Effective is the Shorts Transformation of Traditional Media? An Analysis from the Perspective of User-Generated Content}, booktitle = {Computer Supported Cooperative Work and Social Computing}, year = {2024}, doi = {10.1007/978-981-96-2373-0_9}, publisher = {Springer Nature Singapore}, address = {Singapore}, pages = {124--137}, isbn = {978-981-96-2373-0} } -
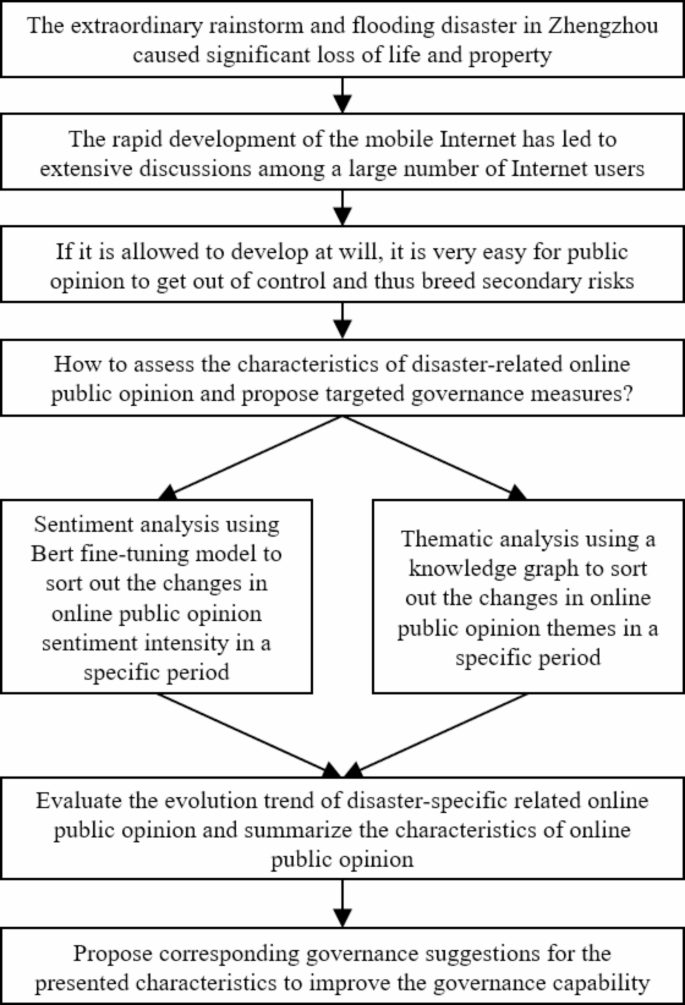 Study on the evolution of online public opinion and government response strategies for the “7–20” extraordinary rainstorm and flooding disaster in Zhengzhou, ChinaPu Zhang, Hao Zhang, and Feng KongNatural Hazards, Sep 2024
Study on the evolution of online public opinion and government response strategies for the “7–20” extraordinary rainstorm and flooding disaster in Zhengzhou, ChinaPu Zhang, Hao Zhang, and Feng KongNatural Hazards, Sep 2024Disaster-related online public opinion develops rapidly,the actual situation is complex and volatile,and the public opinion environment should be regulated through appropriate guidance. 2021 Zhengzhou 7–20 extraordinary rainstorm and flooding disaster has attracted widespread public attention. In order to analyze the online public opinion triggered by extraordinary rainstorm disasters and propose targeted management measures so as to improve the comprehensive disaster reduction efficiency. This paper collected information about the “Zhengzhou rainstorm” posted on the Sina Weibo platform from July 11 to August 14,2021. We analyzed the characteristics of related Weibo from two dimensions: sentiment analysis and thematic analysis. The results are as follows: Online public opinion will be generated rapidly and last for a long time; the different emotional colors change at different periods of the disaster; the focus of online public opinion discussion varies at different periods of the disaster. Given this result,the following suggestions are made: the cooperation level between departments should be improved,and an early warning mechanism for public opinion should be established so that once the relevant public opinion is generated,a quick response can be made; a relevant responsibility mechanism should be established to realize that a specific department is responsible for the handling of public opinion in the corresponding section,to realize a scientific and practical normalized control mechanism for public opinion; Relevant departments should improve the openness and transparency of appropriate handling methods,to establish a public opinion control and guidance mechanism. This study has specific significance for improving the level of governance of online public opinion caused by sudden natural disasters.
@article{PZHANG03, author = {Zhang, Pu and Zhang, Hao and Kong, Feng}, title = {Study on the evolution of online public opinion and government response strategies for the “7–20” extraordinary rainstorm and flooding disaster in Zhengzhou, China}, volume = {121}, issn = {1573-0840}, url = {http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s11069-024-06904-7}, doi = {10.1007/s11069-024-06904-7}, number = {3}, journal = {Natural Hazards}, publisher = {Springer Science and Business Media LLC}, year = {2024}, month = sep, pages = {2849–2872} } -
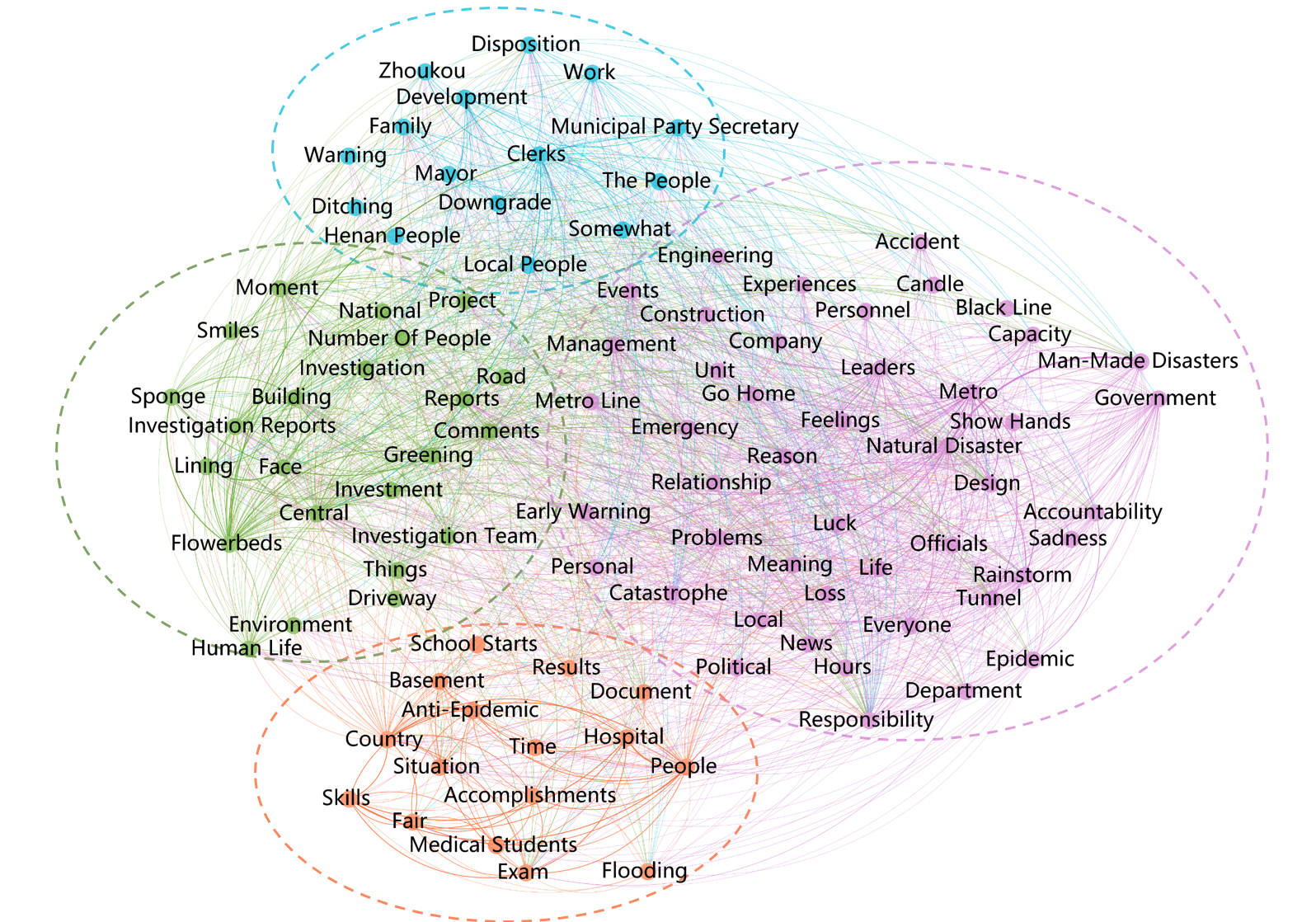 Research on online public opinion in the investigation of the “7–20” extraordinary rainstorm and flooding disaster in Zhengzhou, ChinaPu Zhang, Hao Zhang, and Feng KongInternational Journal of Disaster Risk Reduction, Sep 2024
Research on online public opinion in the investigation of the “7–20” extraordinary rainstorm and flooding disaster in Zhengzhou, ChinaPu Zhang, Hao Zhang, and Feng KongInternational Journal of Disaster Risk Reduction, Sep 2024Sorting out the changing characteristics of online public opinion triggered by a series of events in the investigation and assessment of major natural disasters is of great practical significance for optimizing the work of disaster investigation and assessment, governing the ecology of online public opinion, and enhancing the effect of comprehensive disaster reduction. In this paper, we collected relevant comments from several official media accounts, such as People’s Daily, and evaluated their emotional color using a sentiment analysis method based on the BERT fine-tuning model. Furthermore, keyword co-occurrence semantic network theme analysis is conducted for texts presenting negative emotional overtones to assess the changes in public opinion hotspots. The impact of the relevant online public opinion characteristics and the release of the disaster investigation report on them was assessed in the context of the investigation report itself. Based on sorting out the characteristics of online public opinion on several related topics, targeted public opinion governance initiatives and relevant suggestions for improving the disaster investigation system are proposed. This paper is of positive significance for studying disaster public opinion and improving the effectiveness of emergency management of rainstorms and flooding disasters.
@article{PZHANG02, title = {Research on online public opinion in the investigation of the “7–20” extraordinary rainstorm and flooding disaster in Zhengzhou, China}, journal = {International Journal of Disaster Risk Reduction}, volume = {105}, pages = {104422}, year = {2024}, issn = {2212-4209}, dimensions = {true}, url = {https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S2212420924001845}, doi = {10.1016/j.ijdrr.2024.104422}, author = {Zhang, Pu and Zhang, Hao and Kong, Feng}, keywords = {Rainstorm and flooding disaster, Disaster investigation report, Disaster opinion research, Integrated disaster mitigation, Natural language processing}, }
2023
-
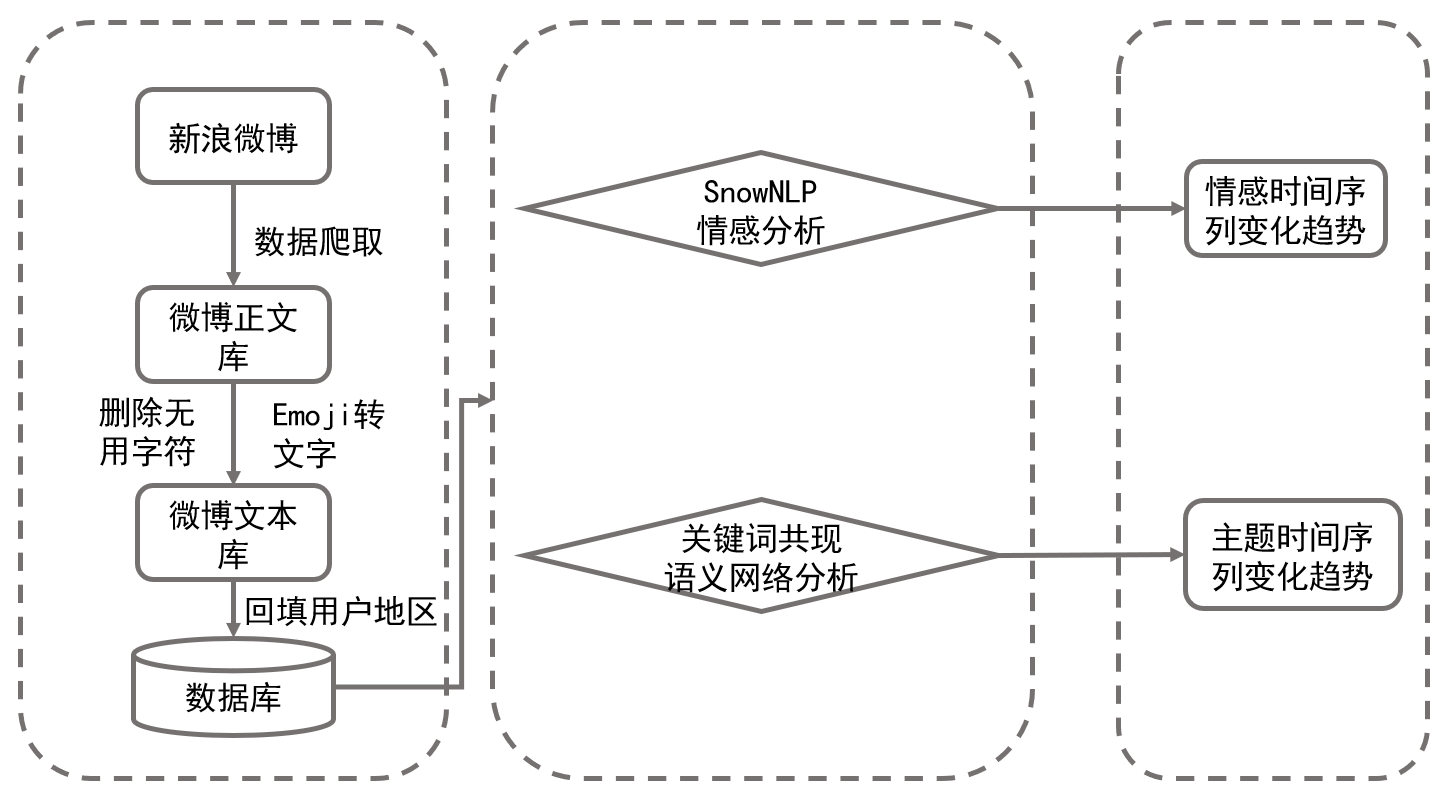 基于微博数据的暴雨洪涝灾害舆情特征研究:以2021年中国三场暴雨洪涝为例张谱, 张豪, 孔锋, and 1 more author水利水电技术(中英文), Sep 2023
基于微博数据的暴雨洪涝灾害舆情特征研究:以2021年中国三场暴雨洪涝为例张谱, 张豪, 孔锋, and 1 more author水利水电技术(中英文), Sep 2023[Objective] The governance of public opinion related to natural disasters is an important element of comprehensive disaster reduction. In order to explore the characteristics of network public opinion triggered by extraordinary rainstorm and flooding disasters, and summarize the experience of relevant public opinion response, [Methods] the three extraordinary rainstorm and flooding disasters that occurred in 2021 were taken as examples and Weibo data related to the topics of “Shanxi rainstorm”, “Henan rainstorm” and “Hubei rainstorm” posted on the Sina Weibo platform were collected. A machine learning method based on the BERT fine-tuning model was used for sentiment analysis on time series to sort out the changes in the hotness and sentiment intensity of disaster public opinion issues; and a knowledge graph method with keyword co-occurrence semantic network as the core explored the characteristics of changes in public opinion hotspots for different disasters. [Results] The results show that(1) public opinion on the same type of rainstorm and flooding disasters usually has similar chronological characteristics, it usually lasts for a long time and the peaks of public opinion are associated with critical events.(2) The emotional color distribution of public opinion on the same type of rainstorm and flooding disasters is similar but will change accordingly depending on the severity of the disaster. The percentage of positive emotion in the Shanxi rainstorm in this study is 36.83% and 28.81% of negative emotion; in the Henan rainstorm, it is 34.23% and 43.25%; in the Hubei rainstorm, it is 45.91% and 27.07%.(3) Public opinion on similar rainstorm and flooding disasters has similar thematic distribution, which can be divided into concerns about the disaster-causing factors and the disaster itself, concerns about the disaster-causing process and emergency rescue and relief, and concerns about the socioeconomic and ecological impacts of the floods. [Conclusion] The evolutionary characteristics of online public opinion triggered by rainstorm and flooding disasters are roughly similar but show some differences due to the difference in the severity of the disasters. In response to this characteristic, the following recommendations are made:(1) daily public opinion control measures and timely response to sudden disasters should be done well;(2) the timely release of official disaster information and reasonably channel and regulate public opinion should be taken seriously;(3) a public opinion control linkage mechanism should be established and excellent management experiences should be learned. The research results are of positive significance to study and judge the changing trends of disaster public opinion and improve the disaster public opinion governance system and capacity.
@article{SJWJ202302005, author = {张谱 and 张豪 and 孔锋 and 孔赟珑}, title = {基于微博数据的暴雨洪涝灾害舆情特征研究:以2021年中国三场暴雨洪涝为例}, journal = {水利水电技术(中英文)}, volume = {54}, pages = {47-59}, year = {2023}, issn = {1000-0860}, doi = {10.13928/j.cnki.wrahe.2023.02.005} }